The Silent Guardian
In the heart of industrial automation, where power surges, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and ground potential differences lurk as silent saboteurs, one unsung hero keeps systems safe and communication stable: optoisolation.
While often overlooked in the design phase, optoisolators (also known as optocouplers) are a fundamental requirement for any reliable industrial-grade device. Without them, even the most sophisticated embedded system can become vulnerable to catastrophic failure — not because of poor logic, but because of poor isolation.
What is Optoisolation?
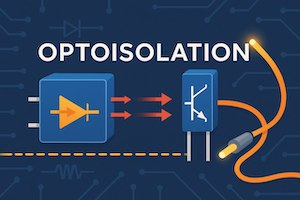
Optoisolation is a method of achieving galvanic isolation between different parts of an electronic system using light. An optoisolator contains a light-emitting diode (LED) and a photosensitive element (typically a phototransistor) housed in a single package. When an electrical signal is applied, the LED emits light, which is detected on the other side — without any physical electrical connection.
Where Optoisolation Makes the Difference
At Atreyo, our focus on IoT, industrial automation, and embedded systems requires rock-solid communication in demanding conditions. Optoisolators are standard in our:
- RS-232 / RS-485 interfaces
- CAN transceivers
- Sensor inputs
- Power control modules
- Modbus and MQTT edge devices
In these applications, optoisolation not only protects internal circuitry but also:
- Reduces noise coupling
- Prevents ground loop currents
- Allows safe interfacing with external devices from different power domains
Optoisolation and System Longevity
Reliability is everything in industrial applications. System downtime costs money. Device failure due to electrical stress isn’t just inconvenient — it can halt operations, damage reputation, and even pose safety risks.
By implementing optoisolation as a design standard, we elevate the MTBF (mean time between failures) and ensure that our systems stay online in the most demanding environments.
Conclusion
As engineers and innovators, we often focus on performance, processing power, and connectivity. But true resilience starts at the interface level. Optoisolation is not an optional extra — it's a core design principle that separates hobby-grade from industrial-grade.
In a world increasingly reliant on connected machines and intelligent infrastructure, optoisolation is a quiet shield that allows all devices to work in harmony and without interference.